Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease that affects millions of people worldwide each year. This illness, caused by the dengue virus, poses significant health risks, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. Understanding its symptoms, prevention methods, and treatment options is crucial for safeguarding your health and the well-being of your community.
Dengue fever has become a growing concern in recent years due to its rapid spread and increasing incidence rates. The disease is primarily transmitted through the bite of an infected Aedes aegypti mosquito, making it a significant public health challenge. This article aims to provide comprehensive insights into dengue fever, equipping readers with the knowledge needed to prevent and manage this potentially life-threatening condition.
As we delve deeper into the subject, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of dengue fever. Additionally, we will highlight preventive measures and strategies to mitigate its spread. By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of how to protect yourself and your loved ones from this dangerous illness.
Read also:Where Is Michael Schiavo Today Unveiling The Truth Behind The Mystery
Table of Contents
- What is Dengue Fever?
- Causes of Dengue Fever
- Symptoms of Dengue Fever
- Diagnosis of Dengue Fever
- Treatment Options
- Prevention Methods
- Dengue Fever Statistics
- Global Impact of Dengue Fever
- Research and Development
- Conclusion
What is Dengue Fever?
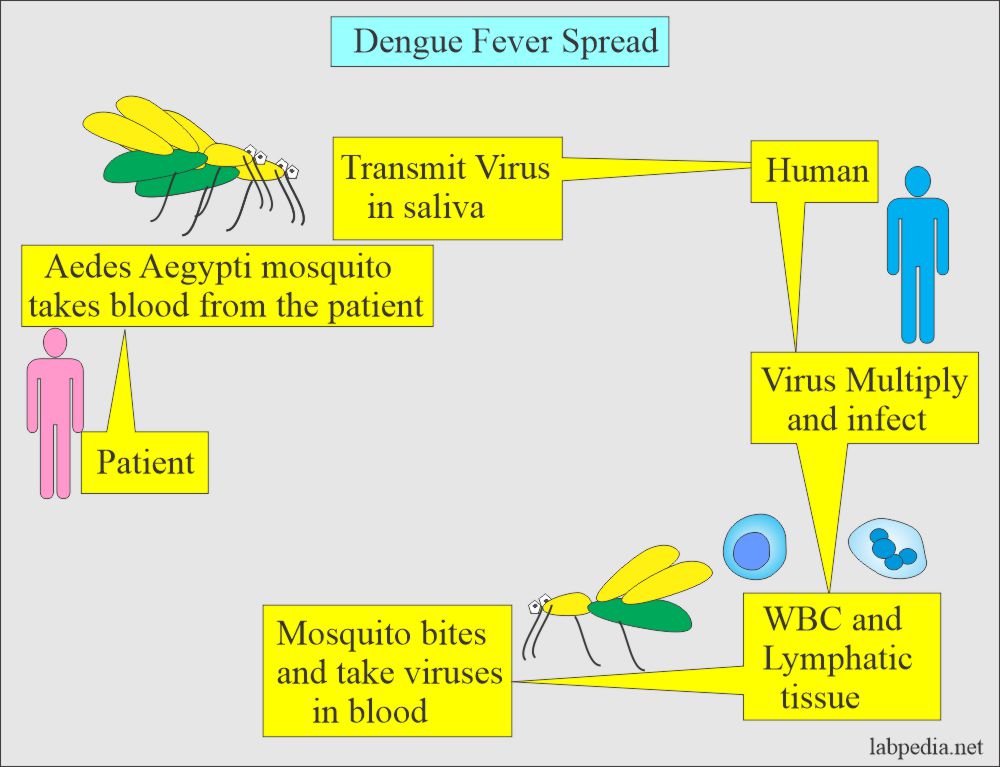
Dengue fever is a viral infection spread by mosquitoes, primarily the Aedes aegypti species. It is characterized by flu-like symptoms, including high fever, severe headache, pain behind the eyes, joint and muscle pain, and rash. In severe cases, it can progress to dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome, which can be fatal if not treated promptly.
This disease is prevalent in urban and semi-urban areas of tropical and subtropical regions, particularly in Southeast Asia, the Pacific Islands, the Caribbean, Central and South America, and parts of Africa. The virus exists in four distinct serotypes, meaning recovery from one type provides immunity only to that specific serotype, leaving individuals susceptible to infection from the others.
Key Facts About Dengue Fever
- Dengue fever is caused by the dengue virus, transmitted by the Aedes aegypti mosquito.
- It affects millions of people globally, with an estimated 100-400 million infections annually.
- Severe cases can lead to life-threatening complications, such as dengue hemorrhagic fever.
Causes of Dengue Fever
The primary cause of dengue fever is the dengue virus, which belongs to the Flavivirus genus. The virus is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected Aedes aegypti mosquito. These mosquitoes typically breed in stagnant water and are most active during the early morning and late afternoon.
Once bitten, the virus enters the bloodstream, leading to infection. The transmission cycle begins when a mosquito bites a person infected with the dengue virus and subsequently bites another person, spreading the virus further. This cycle contributes to the rapid spread of dengue fever in densely populated areas.
Factors Contributing to the Spread of Dengue Fever
- Urbanization and inadequate waste management leading to stagnant water accumulation.
- Climate change, which extends the breeding season of mosquitoes.
- Increased international travel and migration, facilitating the spread of the virus across borders.
Symptoms of Dengue Fever
The symptoms of dengue fever typically appear 4-10 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. The illness usually begins with a sudden high fever, accompanied by other flu-like symptoms. Common symptoms include:
- High fever (up to 104°F or 40°C)
- Severe headache
- Pain behind the eyes
- Muscle and joint pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Rash
In severe cases, symptoms may worsen, leading to dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome. These conditions are characterized by bleeding, low platelet count, and circulatory collapse, requiring immediate medical attention.
Read also:Is Luke Combs A Republican Or Democrat Exploring The Country Stars Political Views
Diagnosis of Dengue Fever
Diagnosing dengue fever involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers assess the patient's symptoms, travel history, and exposure to mosquitoes. Laboratory tests, such as blood tests, are used to detect the presence of the dengue virus or antibodies against it.
Common diagnostic tests include:
Types of Laboratory Tests
- NS1 antigen test: Detects the presence of the dengue virus in the early stages of infection.
- IgM and IgG antibody tests: Identify antibodies produced in response to the virus.
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test: Detects the genetic material of the virus for confirmation.
Treatment Options
Currently, there is no specific medication to treat dengue fever. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. Patients are advised to rest, stay hydrated, and take over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen to reduce fever and pain. However, aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) should be avoided, as they can increase the risk of bleeding.
In severe cases, hospitalization may be required for close monitoring and supportive care, including intravenous fluids and blood transfusions if necessary. Early recognition and prompt medical intervention are critical in managing severe dengue fever.
Prevention Methods
Preventing dengue fever involves controlling the mosquito population and avoiding mosquito bites. Effective prevention strategies include:
Personal Protective Measures
- Using mosquito repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus.
- Wearing long-sleeved clothing and pants to minimize exposed skin.
- Using mosquito nets while sleeping, especially in high-risk areas.
Environmental Control Measures
- Eliminating standing water sources where mosquitoes can breed.
- Covering water storage containers and properly disposing of waste.
- Implementing community-wide mosquito control programs, such as fogging and larviciding.
Dengue Fever Statistics
Dengue fever is a significant global health issue, with an estimated 100-400 million infections occurring annually. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 500,000 people require hospitalization each year due to severe dengue, with a significant number of fatalities reported in some regions.
The disease's incidence has increased dramatically over the past few decades, with a 30-fold increase in cases since the 1960s. This trend is attributed to urbanization, climate change, and increased global travel, which facilitate the spread of the virus.
Global Impact of Dengue Fever
The global impact of dengue fever extends beyond health, affecting economic and social aspects of affected communities. The economic burden of dengue fever includes healthcare costs, loss of productivity, and expenses related to mosquito control programs. Developing countries, in particular, face significant challenges in addressing the disease due to limited resources and infrastructure.
Efforts to combat dengue fever require coordinated action at local, national, and international levels. Public health initiatives, such as education campaigns and research into new vaccines and treatments, are essential in reducing the disease's impact.
Research and Development
Research into dengue fever continues to advance, with a focus on developing effective vaccines and treatments. Several vaccines have been developed, including CYD-TDV (Dengvaxia), which has shown promising results in reducing the incidence of severe dengue and hospitalizations. However, challenges remain in ensuring vaccine safety and efficacy across all populations.
Emerging technologies, such as genetically modified mosquitoes and Wolbachia bacteria, offer innovative approaches to controlling the mosquito population and reducing dengue transmission. Continued investment in research and development is crucial in overcoming the challenges posed by dengue fever.
Conclusion
Dengue fever is a serious global health concern that requires collective action to address. By understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment, individuals and communities can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this illness. Implementing effective prevention strategies and supporting ongoing research efforts are vital in reducing the disease's impact worldwide.
We encourage readers to share this article and spread awareness about dengue fever. Together, we can work towards a future where the threat of dengue fever is minimized, ensuring healthier and safer communities for all. For more information on dengue fever and other health topics, explore our website and stay informed.